SparkSQLRDDs
3364
RDDs
Spark支持两种方法将存在的RDDs转换为SchemaRDDs。第一种方法使用反射来推断包含特定对象类型的RDD的模式(schema)。在你写spark程序的同时,当你已经知道了模式,这种基于反射的方法可以使代码更简洁并且程序工作得更好。
创建SchemaRDDs的第二种方法是通过一个编程接口来实现,这个接口允许你构造一个模式,然后在存在的RDDs上使用它。虽然这种方法更冗长,但是它允许你在运行期之前不知道列以及列的类型的情况下构造SchemaRDDs。
利用反射推断模式
Spark SQL的Scala接口支持将包含样本类的RDDs自动转换为SchemaRDD。这个样本类定义了表的模式。
给样本类的参数名字通过反射来读取,然后作为列的名字。样本类可以嵌套或者包含复杂的类型如序列或者数组。这个RDD可以隐式转化为一个SchemaRDD,然后注册为一个表。表可以在后续的sql语句中使用。
// sc is an existing SparkContext.
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
// createSchemaRDD is used to implicitly convert an RDD to a SchemaRDD.
import sqlContext.createSchemaRDD
// Define the schema using a case class.
// Note: Case classes in Scala 2.10 can support only up to 22 fields. To work around this limit,
// you can use custom classes that implement the Product interface.
case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
// Create an RDD of Person objects and register it as a table.
val people = sc.textFile("examples/src/main/resources/people.txt").map(_.split(",")).map(p => Person(p(0), p(1).trim.toInt))
people.registerTempTable("people")
// SQL statements can be run by using the sql methods provided by sqlContext.
val teenagers = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name FROM people WHERE age >= 13 AND age <= 19")
// The results of SQL queries are SchemaRDDs and support all the normal RDD operations.
// The columns of a row in the result can be accessed by ordinal.
teenagers.map(t => "Name: " + t(0)).collect().foreach(println)编程指定模式
当样本类不能提前确定(例如,记录的结构是经过编码的字符串,或者一个文本集合将会被解析,不一样的字段投影给不一样的用户),一个SchemaRDD可以通过三步来创建。
- 从原来的RDD创建一个行的RDD
- 创建由一个
StructType表示的模式与第一步创建的RDD的行结构相匹配 - 在行RDD上通过
applySchema方法应用模式
// sc is an existing SparkContext.
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
// Create an RDD
val people = sc.textFile("examples/src/main/resources/people.txt")
// The schema is encoded in a string
val schemaString = "name age"
// Import Spark SQL data types and Row.
import org.apache.spark.sql._
// Generate the schema based on the string of schema
val schema =
StructType(
schemaString.split(" ").map(fieldName => StructField(fieldName, StringType, true)))
// Convert records of the RDD (people) to Rows.
val rowRDD = people.map(_.split(",")).map(p => Row(p(0), p(1).trim))
// Apply the schema to the RDD.
val peopleSchemaRDD = sqlContext.applySchema(rowRDD, schema)
// Register the SchemaRDD as a table.
peopleSchemaRDD.registerTempTable("people")
// SQL statements can be run by using the sql methods provided by sqlContext.
val results = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name FROM people")
// The results of SQL queries are SchemaRDDs and support all the normal RDD operations.
// The columns of a row in the result can be accessed by ordinal.
results.map(t => "Name: " + t(0)).collect().foreach(println)原文链接: https://www.yukx.com/bigdata/article/details/847.html 优科学习网SparkSQLRDDs
推荐文章
-
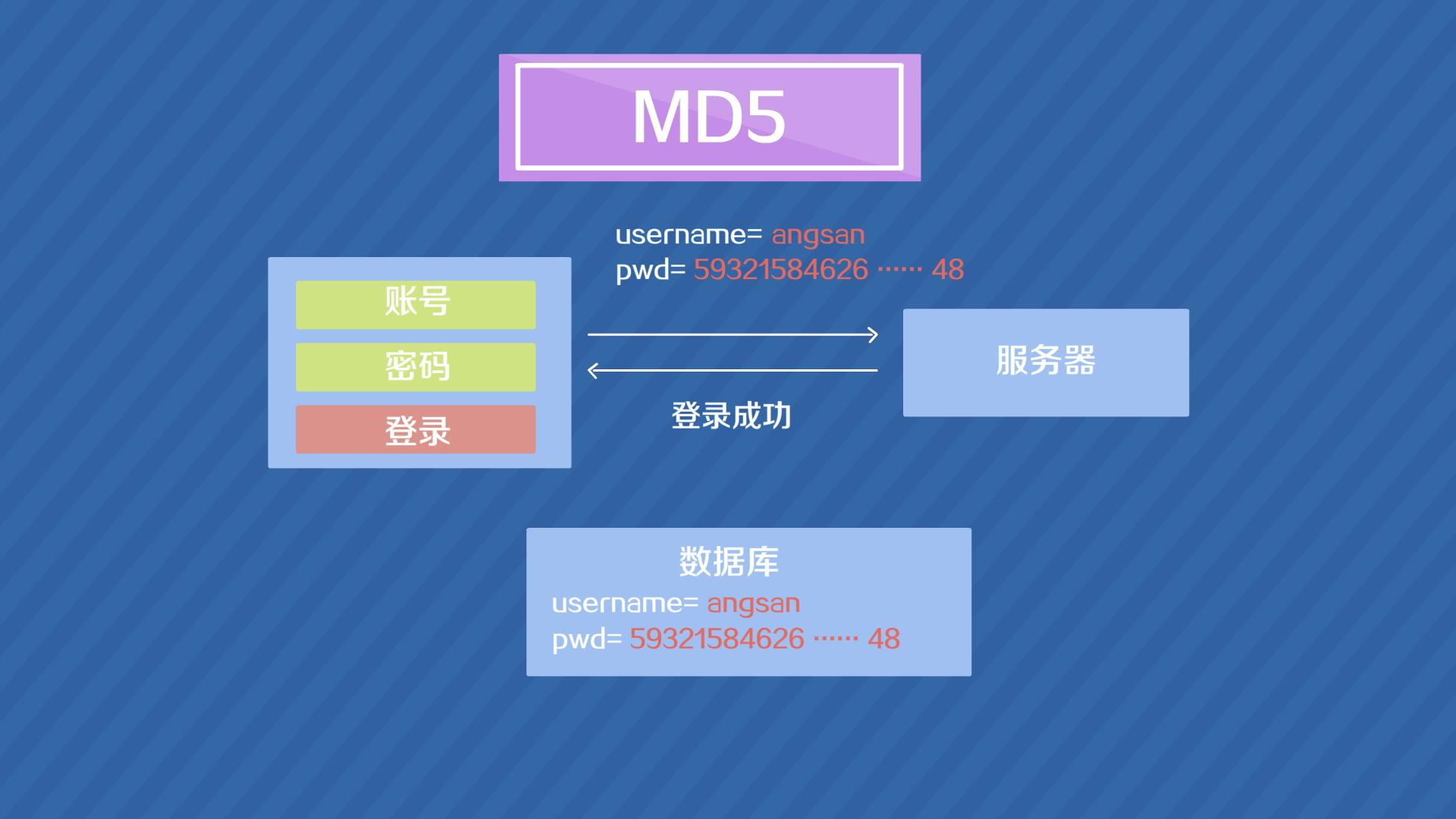 MD5(Message-DigestAlgorithm5)是一种广泛使用的散列函数(哈希函数),由美国密码学家罗纳德·李维斯特(RonaldL.Rivest)在1991年设计。MD5的作用是对任意长度的信息生成一个固定长度(128位,即32个十六进制字符)的“指纹”或“消息摘要”,并且几乎不可能找到
MD5(Message-DigestAlgorithm5)是一种广泛使用的散列函数(哈希函数),由美国密码学家罗纳德·李维斯特(RonaldL.Rivest)在1991年设计。MD5的作用是对任意长度的信息生成一个固定长度(128位,即32个十六进制字符)的“指纹”或“消息摘要”,并且几乎不可能找到 -
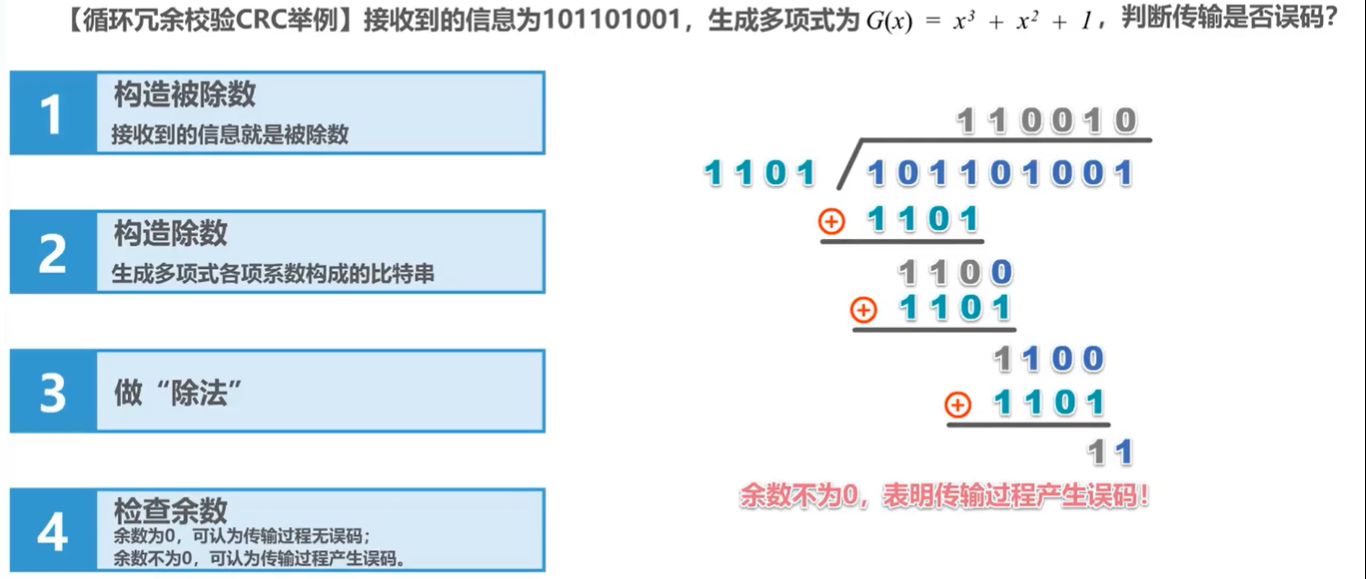 循环冗余校验(CyclicRedundancyCheck,CRC)是一种用于检测数据传输和存储过程中发生错误的技术,属于一种基于数学原理的错误检测编码(ErrorDetectionCoding)方法。它通过在原始数据上附加一个固定长度的校验码,使得接收端可以通过同样的计算规则对收到的数据进行校验,确
循环冗余校验(CyclicRedundancyCheck,CRC)是一种用于检测数据传输和存储过程中发生错误的技术,属于一种基于数学原理的错误检测编码(ErrorDetectionCoding)方法。它通过在原始数据上附加一个固定长度的校验码,使得接收端可以通过同样的计算规则对收到的数据进行校验,确 -
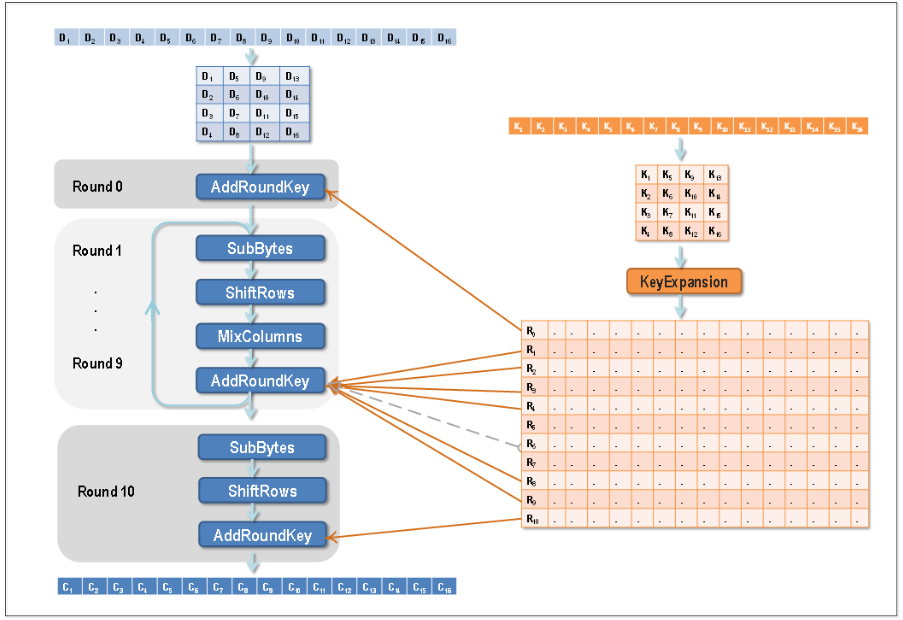 AES(AdvancedEncryptionStandard)是一种广泛使用的对称密钥加密算法,它是美国国家标准与技术研究院(NIST)于2001年制定的加密标准,用于替代原有的DES(DataEncryptionStandard)。AES算法以其高效性、安全性和可靠性而著称,在众多应用领域中被广泛
AES(AdvancedEncryptionStandard)是一种广泛使用的对称密钥加密算法,它是美国国家标准与技术研究院(NIST)于2001年制定的加密标准,用于替代原有的DES(DataEncryptionStandard)。AES算法以其高效性、安全性和可靠性而著称,在众多应用领域中被广泛 -
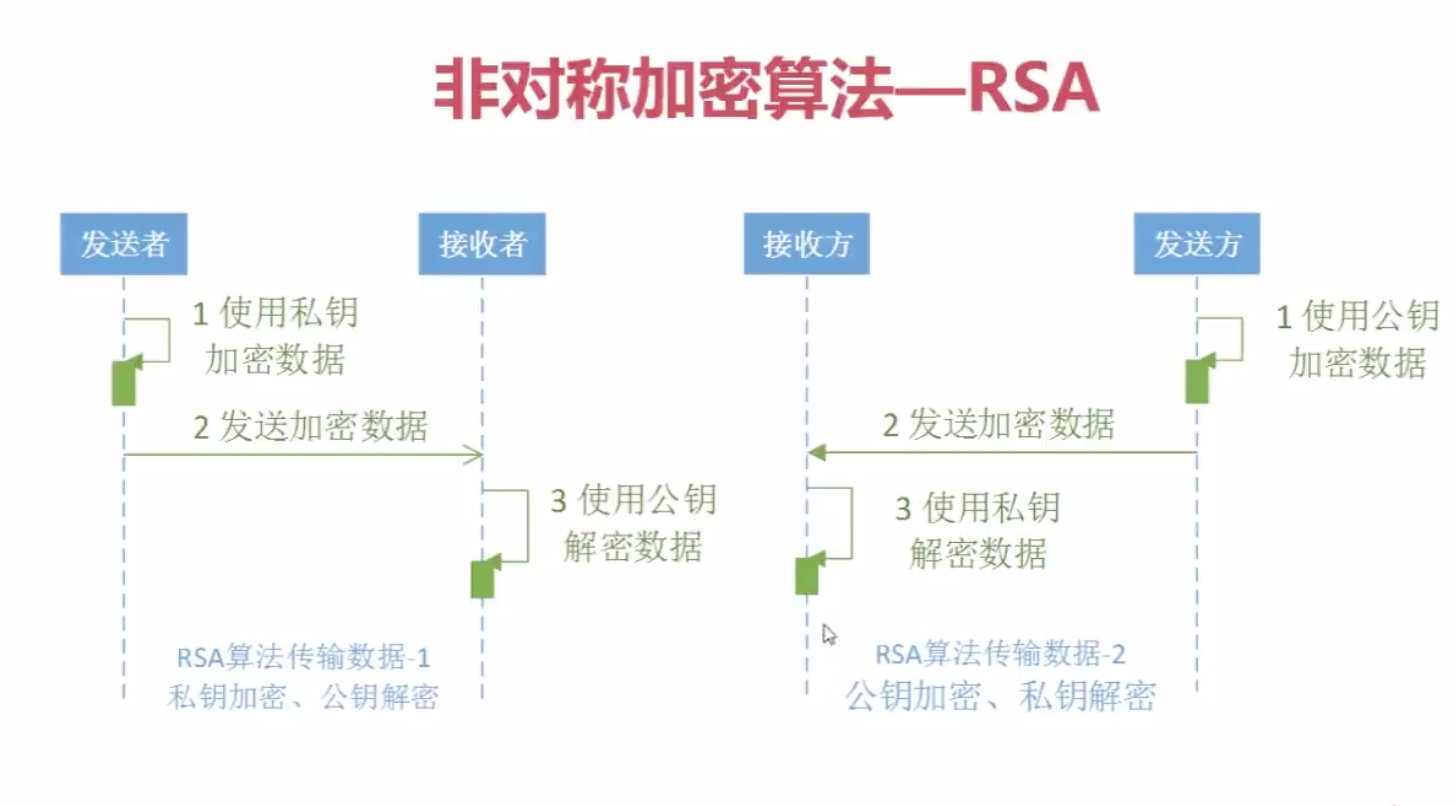 RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)是一种广泛应用的非对称加密算法,由RonRivest、AdiShamir和LenAdleman在1977年提出。其安全性基于数学上的大数因子分解难题,即对于足够大的两个素数p和q而言,已知它们的乘积很容易,但想要从这个乘积中恢复原始的素数则异常困难
RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)是一种广泛应用的非对称加密算法,由RonRivest、AdiShamir和LenAdleman在1977年提出。其安全性基于数学上的大数因子分解难题,即对于足够大的两个素数p和q而言,已知它们的乘积很容易,但想要从这个乘积中恢复原始的素数则异常困难 -
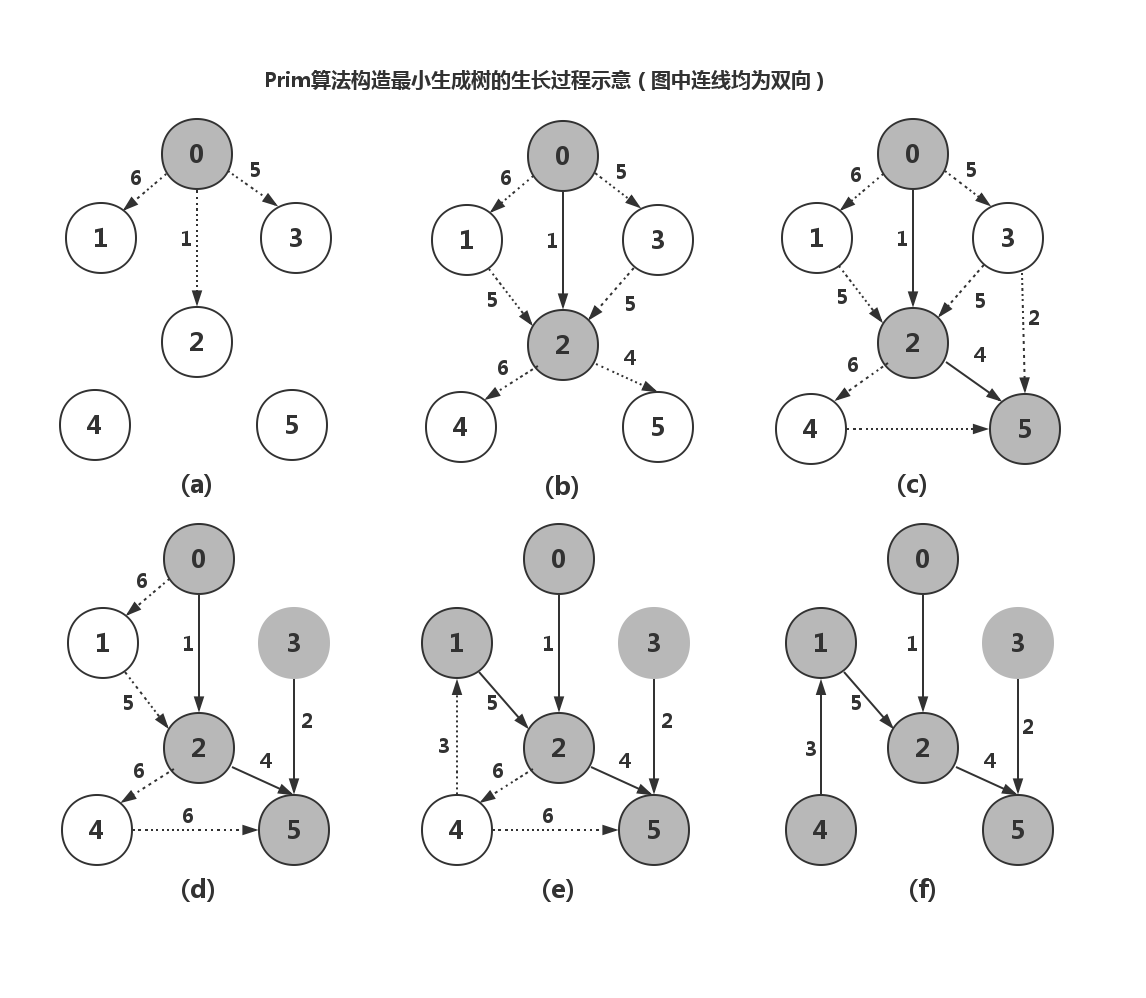 最小生成树(MinimumSpanningTree,MST)是一种图论算法,用于在一个带权重的无向连通图中找到一棵包括所有顶点且总权重尽可能小的树。常见的最小生成树算法有两种:Prim算法和Kruskal算法。Prim算法原理:Prim算法是一种贪心算法,它从图中的一个顶点开始,逐步增加边,每次都添
最小生成树(MinimumSpanningTree,MST)是一种图论算法,用于在一个带权重的无向连通图中找到一棵包括所有顶点且总权重尽可能小的树。常见的最小生成树算法有两种:Prim算法和Kruskal算法。Prim算法原理:Prim算法是一种贪心算法,它从图中的一个顶点开始,逐步增加边,每次都添 -
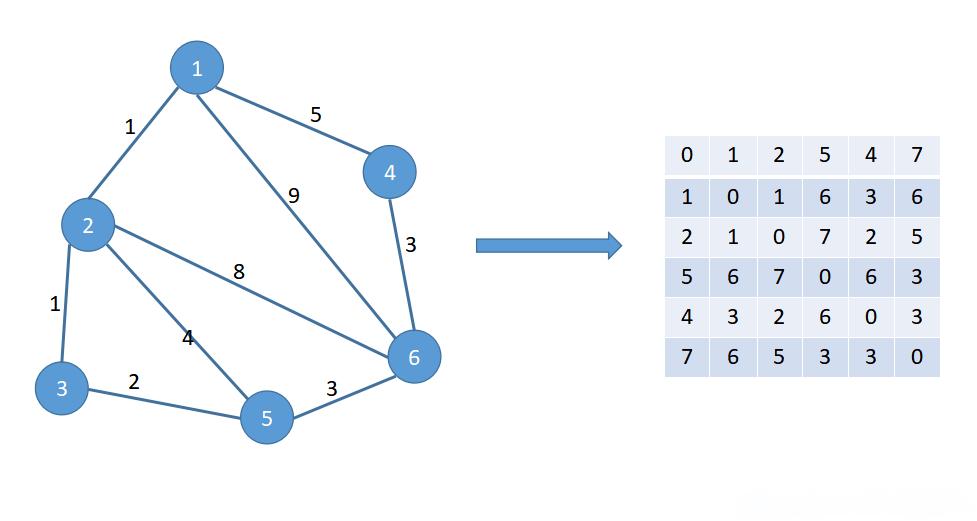 关于最短路径算法的Java实现,这里简述一下几种常用的算法及其基本原理,并给出一个Dijkstra算法的基本实现框架。Dijkstra算法(适用于无负权边的图)Dijkstra算法用于寻找图中一个顶点到其他所有顶点的最短路径。它维护了一个距离表,用来存储从源点到各个顶点的已知最短距离,并且每次都会选
关于最短路径算法的Java实现,这里简述一下几种常用的算法及其基本原理,并给出一个Dijkstra算法的基本实现框架。Dijkstra算法(适用于无负权边的图)Dijkstra算法用于寻找图中一个顶点到其他所有顶点的最短路径。它维护了一个距离表,用来存储从源点到各个顶点的已知最短距离,并且每次都会选
学习大纲
编程指南
快速上手
Spark RDDs
Spark Streaming
基本概念
Spark Streaming性能调优
Spark SQL
Spark SQL数据源
SparkSQLRDDs
GraphX编程指南

